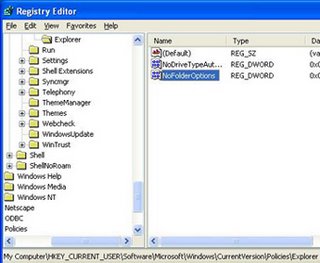
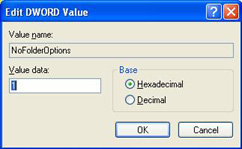
Windows Vista will be released on January 30 2007.
Minimum System Requirements:
Processor: 800 MHz 32 bit or 64 bit
System memory: 512 MB
GPU: SVGA (800x600)
HDD: 20 GB
HDD Free Space: 15 GB
Optical Drive: CD ROM Drive
A graphics Processor that is DirectX9 cabable is better for good Windows Vista experience.
System Requirements to get an even better Windows Vista Experience:
Processor: 1 GHz 32 bit or 64 bit
System Memory: 1 GB
3D Graphics card: Minimum 128 MB DirectX9 capable card with Pixel Shader 2.0 support and 32 bits per pixel.
HDD: 40 GB
HDD Free Space: 15 GB
Optical Drive: DVD ROM Drive
Audio Output capability
Internet Access capability
Features:
1.Start Menu
The start menu of Windows Vista is faster and more helpful than previous Windows versions. The start menu has a new feature called Instant search which can help you find anything on your PC. The new start menu makes it easy for you to navigate across all of the installed applications on your PC.
2.Security
Windows Vista contains new security features. Your PC will be protected from Worms,Spyware,Viruses and other unwanted software. Windows Vista's security features prevent Malware from installing,find and remove Malware if it has already been installed.
Automatic Updates and Windows Security Center will keep your PC up to date with the latest security patches, and also alert you when your PC needs to install an update. Windows Vista Firewall protect your PC from Hackers. Windows Defender protect your PC from Spyware and other unwanted software.The Malacious Software Removal Tool periodically scans your PC for Viruses. You can also keep your computer healthy by using Windows OneCare antivirus software.
3.Search Folders
Windows Vista introduces a powerful new tool Search Folders that makes it easy to find and organize your files-wherever they may be on your PC. A Search Folder is simply a search that you save. Opening a Search Folder instantly runs that saved search, displaying up-to-date results immediately.
4.Windows Internet Explorer 7.0
Windows Vista has Internet Explorer 7.0 version. I.E 7.0 has new Security and privacy features. Also it has so many features like Tabbed browsing,inline search,and shrink to fit printing etc. All these features makes everyday tasks easier.
5.System Restore
In Windows Vista, System Restore allows recovery from a greater range of changes than in Windows XP. The file filter system for system restore used in previous versions of Windows is replaced with a new approach.
Windows vista provides a backup experience that is easier to use with more choices for storing your backed up information. You can choose to back up to CD-ROM, DVD-ROM, an external hard disk connected to your PC by USB or IEEE 1394, another hard disk on your PC, or to another PC or server connected to your network.
6.Networking
Windows Vista networking is easier to setup,easier to use,and more secure and reliable. We can connect wirelessly to our company's network,copy files between computers,share an internet connection and printers etc.
7.Speech Recognition in Windows Vista
You can interact with your computer using your voice with Windows Speech recognition feature. This is a new feature in Windows Vista. We can dictate documents and e-mails,use voice commands to start and switch between applications,control the operating system and even fill out forms on the web. The accuracy with which Windows Vista recognizes your speech improves each time you use it. Windows Speech Recognition was built using the latest Microsoft speech technologies.
Windows Vista supports speech recognition in English (United States),English (United Kingdom),German, French,Spanish,Japanese,Traditional Chinese and Simplified Chinese languages.
Also there are so many new features in Windows Vista O.S. All we make our PC ready for Windows Vista.